Hanson Robotics’ most advanced AI-powered robot, Sophia

As the world’s first robot citizen, and the first robot Innovation Ambassador for the United Nations Development Programme, Sophia is a global name having made appearances in worldwide conferences as well as daytime TV shows in many countries. The unique blend of technology acts as a framework for cutting edge robotics and AI research, particularly for understanding human-robot interactions and their potential service and entertainment applications.
Here, we look at how Sophia has been developed over the years.
2007 – Founding of pioneering robot company, Hanson Robotics
Hanson Robotics was founded in 2007 by David Hanson and was originally based in Texas. Since its founding 15 years ago, the team has built a worldwide reputation for creating human-like robots. Hanson founded the company to pursue his fascination with art, science fiction and philosophy that pushed him to think about what the future of robots could look like
2016 – Activating Sophia the robot
In February of 2016, Hanson Robotics activated Sophia and the robot made its first public appearance in mid-March of the same year. Just one year later, Sophia was given Saudi Arabian citizenship, becoming the first robot to receive citizenship of any country. One month later, Sophia was named the United Nations Development Programme's first Innovation Champion.
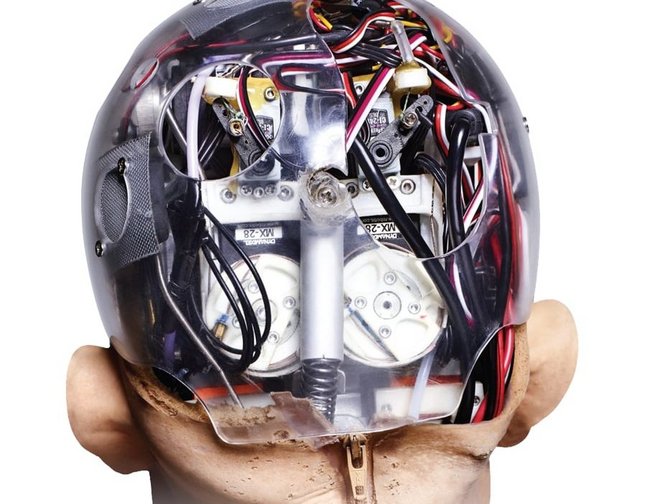

2018 – Adding more AI features to Sophia
As of 2018, Sophia's architecture includes scripting software, a chat system, and OpenCog, an AI system designed for general reasoning. In the same year, Sophia was upgraded with functional legs and the ability to walk.
Hanson also embedded Alphabet’s speech recognition technology which is designed to get smarter over time. With this technology, Hanson hoped Sophia would be a suitable companion for the elderly at nursing homes or be used to help crowds at large events or parks.
2019 – Creating ‘Little Sophia’
Following the launch and activation of Sophia, Hanson Robotics released “Little Sophia” as a companion that could teach children how to code. During the same year, Sophia displayed the ability to create drawings, including portraits displaying the robots ability to improve as it makes more and more interactions.
2021 – Robotics technology joining the metaverse
More recently, it has been announced that a virtual anime version of Sophia will be released in 100 non-fungible tokens that can interact autonomously with people in a gamified environment.
Jeanne Lim, the former CEO of Hanson Robotics, who is now the co-founder and CEO of beingAI, the startup that created Sophia’s official virtual version for the interactive NFT, said she hopes the new AI being will bring together humanity and technology “to help humans attain our true nature of unconditional love and pure possibilities.”1