V7’s pioneering AI solution for detecting melanoma

Founded in late 2018, V7 was born out of the need to programme computers using examples of real-life actions.
“We enable computer scientists to programme machines that learn from examples, such as doctors pointing out lesions, robotic arms picking objects, astronomers pointing out exoplanets and more,” says Alberto Rizzoli, CEO and Co-Founder of V7.
Rizzoli founded the company with Simon Edwards who he met at Hackathon in 2014. The pair decided to found the company four years later “ to allow computers to transition from a world of rule-based systems in code, to training data,” says Rizzoli.
V7 hopes to usher in a new era of living software of models running on continuously evolving data. To do this, the company is looking to make deep learning more robust and easier to develop so that any business can implement state-of-the-art AI from a single platform.
Applying V7’s technology in the European melanoma project
The technology developed by V7 has proven its worth iTobos, an ongoing European mole scanning project.
“iToBoS is a consortium awarded by the EU’s Horizon 2020 program for the sum of €12mn. It’s developing a machine that scans patients and analyses their moles at high resolution to spot anything that could lead to a health risk such as malignant melanoma,” says Rizzoli.
Particularly in the summer months, some people across the world will face an increased risk of skin cancer caused by long exposure to the sun. Skin cancer is the most common human malignancy and its incidence has been increasing in the last decade.
The American Cancer Society estimates about 99,780 new melanomas will be diagnosed (about 57,180 in men and 42,600 in women) in the US in 2022. This statistic is reflected over the pond with melanoma skin cancer incidence rates being projected to rise by 7% in the UK between 2014 and 2035, to 32 cases per 100,000 people by 2035.
iToBoS, or Intelligent Total Body Scanner, aims to build a new diagnostic tool for the early detection of melanoma.
Starting in April 2021, the project will last 48 months until March 2025. Differing from previous technologies that map the surface of human skin for mole classification, iToBoS will photograph each mole at a higher resolution and use additional information to determine the level of melanoma risk for each lesion.
By collecting data from a balanced set of healthy and at-risk patients the study will have more information to create a machine that captures the same image resolution as a dermatoscope that dermatologists use to analyse the skin.
However, this new technology will be able to do this automatically through the robotic movement of cameras, and utilising AI to identify and crop each lesion across the body - while anonymising all patient’s identifiable features.
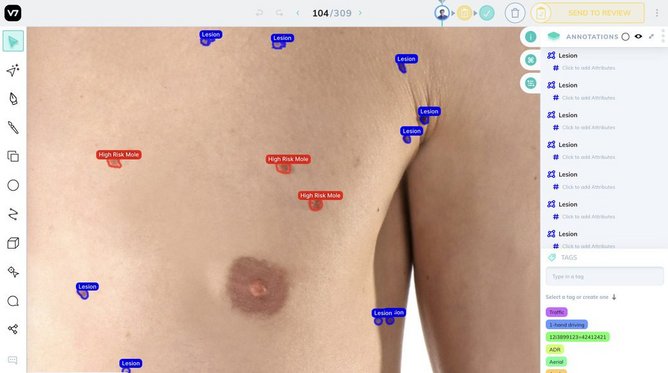
“With iTobos, we are enabling dermatologists to teach and work alongside machines to spot malignant lesions in full body scans. In the study, dermatologists or human “labelers” will be able to point out lesions (moles) and AI models on V7 will periodically assist with the job of spotting them and classifying them,” comments Rizzoli.
He adds: “When 100 examples of an object, such as a benign mole like those we have all over our bodies, is highlighted in the platform using a pen tool, the system is able to spot the rest automatically reducing the effort required by humans, encourages to continue doing so until the AI reaches the maximum accuracy allowed for today’s technology, which continues to evolve and break new records every year.”
Saving lives with V7’s AI-enabled technology
As melanoma selection is difficult at times, AI can condense the world’s dermatological knowledge, composed of annotated images that represent a doctor’s opinion on the mole, into a piece of software.
V7’s technology is used to apply tags to every patient and lesion to accurately represent both demographics and 16 lesion types. This is particularly important as populations that go for mole scans are very imbalanced - it tends to be people from sunny parts of the world visit dermatologists more frequently.
This is why it’s crucial to ensure that the technology is trained on representative samples of people.
“Today going to the dermatologist requires them to manually place a dermoscope on each lesion to capture a picture, which is both time consuming and error prone. With iTobos we can keep a record of previous scans and compare the exact spot where a lesion was identified previously to check whether it has changed in appearance signifying a potential risk, or if a new one has appeared,” says Rizzoli.
He concludes: “Considering the high death risk of malignant melanoma, technologies like iTobos will save lives.”